Contribute
| Go For Exercise Stress Test To Know Your Heart Conditions |
Dr. Indrajeet Tyagi and Dr. Iranna Hirapur
12/14/2025
An exercise stress test is a medical procedure that monitors the heart's electrical activity, blood pressure, and rhythm while a person exercises on a treadmill or stationary bike while hooked up to an EKG to monitor your heart’s activity. This test helps determine how well your heart responds during times when it is working its hardest. It is used to diagnose coronary artery disease, find the cause of symptoms like chest pain, or evaluate the effectiveness of a treatment plan. To prepare, you should not eat or smoke for a few hours before the test and wear comfortable clothing and shoes, and you may need to stop the test at any time due to symptoms or exhaustion. What is a stress test? A stress test is a very commonly performed test to learn: This makes it easier to identify and evaluate certain heart issues, such as: Cardiac stress tests help healthcare providers determine whether you need additional — often more invasive — testing to confirm a diagnosis or if treatment might lower your heart attack risk and make you feel better. How does a stress test work? A heart stress test starts by making your heart pump harder and faster. For many people, this includes walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bicycle. That is why the test is often called an exercise stress test. Healthcare providers assess your response to the increased workload by measuring: You may need this test to detect heart problems. This test may be right for you Why anyone might needs a stress test? Who should have a cardiac stress test? Stress tests are also for people with a heart disease diagnosis who: · Congenital heart disease · Congestive heart failure · Coronary artery disease · Heart valve disease · Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy People with high-risk occupations (like pilots or professional athletes) may also need stress tests · Angina, which is chest pain or discomfort due to poor blood flow to the heart. · Arrhythmia, which is a rapid or irregular heartbeat. · Shortness of breath (dyspnea). · Feeling lightheaded or dizzy. if you have symptoms of heart disease · Would like to start exercising. · Are undergoing treatment and healthcare providers need to determine how well it’s working. · Face a higher risk of complications due to a personal or family history of heart disease. · Have diabetes or other underlying conditions that increase your risk of heart disease. · Require non-cardiac surgery and healthcare providers need to assess your risk of complications. Providers may also do stress tests in people without known heart disease or symptoms to assess their risk for heart disease and heart attacks, especially if they have other risk factors like diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol or a family history of premature heart disease. What are the different types of stress tests? There are many methods for assessing heart function while it is hard at work. All cardiac stress tests involve checking your heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels and electrical activity. However, there are some differences. Stress test types include: 1. Exercise stress test: This is the most common and basic heart stress test. It involves walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bicycle. A well-trained exercise physiologist usually tailors the speed and elevation of the treadmill to your ability to walk and your overall fitness. If you cannot exercise, you receive medications that make your heart pump harder and faster or dilate the artery supplying blood to your heart (coronary arteries). An electrocardiogram (EKG) captures your heart’s electrical activity. Exercise stress tests check for signs of coronary artery disease. 2. Exercise stress echocardiogram: An exercise stress echocardiogram is similar to the basic stress test but provides more detail. Healthcare providers perform an echocardiogram (ultrasound of your heart) before and at peak exercise. This cardiac imaging test uses sound waves to evaluate blood flow through your heart as well as the pumping chambers of your heart (muscle) and valve functions. You might need a stress echocardiogram if the results of your initial stress test are unclear. This study enables healthcare providers to observe blood flow through the heart’s chambers as well as the effects of exercise. 3. Nuclear stress test: This advanced heart stress test uses safe levels of a radioactive substance and a cardiac imaging scan to assess heart function. A healthcare provider takes pictures of your heart before (at rest) and after you exercise. A cardiologist compares the amount of blood flow to the muscle of your heart at rest and after stress. A decrease in blood flow signal usually indicates a blockage in one or multiple arteries in your heart. 4. Nuclear cardiac stress tests can: 1) Determine the severity of blockage of coronary artery disease. 2) Assess whether previous treatments, such as stents or bypass surgery are working, as they should. 3) Help you avoid more invasive heart tests, such as cardiac catheterization. 4) Show whether your heart is healthy enough for non-cardiac surgery or exercise. 5. Cardiac rehabilitation stress test: If your healthcare provider recommends cardiac rehabilitation, the program may include stress testing. Rehabilitation is a medically supervised exercise program that helps people with heart disease become more physically active. Cardiac rehabilitation stress testing includes: 1) Entrance stress test: Helps the rehabilitation team develop an exercise program that’s appropriate for your capabilities. 2) Exit stress test: Enables the team to measure your progress and create a long-term exercise program after you complete rehabilitation.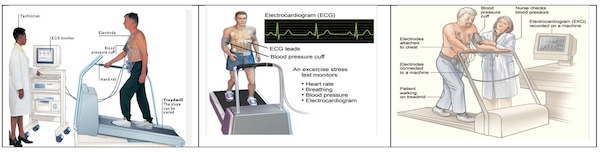
You may also access this article through our web-site http://www.lokvani.com/
