Contribute
| The Next Era Of Cardiovascular Care With AI, Gene Therapy, And Novel Drugs Drive: A Precision Approach |
Dr. Indrajeet Tyagi and Dr. Iranna Hirapur
10/02/2025
The Next Era Of Cardiovascular Care With AI, Gene Therapy, And Novel Drugs Drive: A Precision Approach Gene therapy targets the root cause of inherited heart disease The genetic medicine is now a clinical reality, offering hope for patients with previously untreatable inherited heart conditions. · ATTR-CM treatment: Innovative advancements are occurring in the use of CRISPR gene editing for transthyretin amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM). A one-time infusion of an investigational CRISPR-based therapy has shown significant success in early clinical trials for treating Sickle Cell Disease and Beta-Thalassemia and remarkable efficacy in the TTR protein linked to the disease. ATTR-CM is a progressive heart disease caused by the buildup of amyloid protein in the heart. Treatment options aim to slow disease progression, improve symptoms, and prolong life expectancy. What are the latest research in heart disease? Recent research in heart disease is marked by rapid advancements in gene therapy, artificial intelligence (AI), and pharmaceuticals. Researchers are also focused on personalized medicine and interventions for early risk factors to address the growing global burden of cardiovascular disease. New and refined therapeutic approaches include the following genetic therapies · Gene editing with CRISPR: CRISPR-Cas9 technology is being used in clinical trials to target the TTR gene in the liver for transthyretin amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM). This therapy aims for a one-time treatment that could permanently reduce the production of the misfolded proteins that cause the disease. · Investigational gene therapies: Other gene therapies in trials include NVC-001 for LMNA-related dilated cardiomyopathy (LMNA DCM), RP-A601 for arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (PKP2-ACM), and SGT-501 for catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT). · mRNA therapeutics: Messenger RNA (mRNA) therapy enables the body to make the proteins we need to prevent, treat, or cure diseases. Researches in this area are evaluating an mRNA therapeutic encoding for vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) for patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Pharmacological advancements · Anti-obesity drugs: Anti-obesity medications like semaglutide (Ozempic/Wegovy) and tirzepatide (Mounjaro/Zepbound) have shown significant cardiovascular benefits in addition to weight loss. The SELECT cardiovascular outcomes trial found that semaglutide showed a 20% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events. · Targeted lipid-lowering therapies: Clinical trials are testing new drugs and RNA-targeted technologies like lepodisiran, that dramatically lower lipoprotein(a)—a unique type of "bad cholesterol" linked to heart disease. · Refined SGLT2 inhibitor use: The benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors like dapagliflozin and empagliflozin have been found useful to a wider range of heart failure patients, including those with preserved ejection fraction. · New drug for heart failure: Finerenone (Kerendia) received FDA approval recently to reduce risks in adults with heart failure with ejection fraction of 40% or more, based on results from the FINEARTS-HF trial. · Novel drug for inflammation: The drug colchicine (Lodoco), previously used for gout, was found and approved couple of years ago to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in patients with established coronary artery disease. Procedural innovations · Pulsed field ablation (PFA): PFA has become an effective alternative to traditional catheter ablation for treating atrial fibrillation (AF), with new systems demonstrating comparable efficacy and a better safety profile. Recent studies showcased its use for both paroxysmal AF and scar-related ventricular tachycardia (VT). · Intravascular imaging: Studies suggest that intravascular imaging can improve outcomes for complex stenting procedures in patients with high-risk calcified coronary artery disease. Describe Enhanced prediction and diagnostic tools. Artificial intelligence (AI) · Early detection systems: AI-powered screening tools analyze medical images, such as ECGs, with exceptional accuracy to predict the risk of heart conditions like heart failure than the traditional clinical guidelines. · Real-time monitoring: AI-enabled wearable devices can provide continuous heart monitoring from home and deliver real-time alerts for cardiac abnormalities, which has been shown to reduce hospital admissions for heart failure patients. In atrial fibrillation treatment, AI-driven models like DeePRISM analyze intracardiac waveforms in real-time to enhance the success and safety of catheter ablation. Risk factor assessment · Childhood risk factors: The International Childhood Cardiovascular Cohort (i3C) study provides strong evidence that risk factors during childhood, such as BMI and blood pressure, are directly associated with cardiovascular events in adulthood. · Genetic risk scores: Polygenic risk scores, which analyze multiple genetic variants, are being developed to more precisely identify individuals at high risk for heart disease before symptoms appear. · New risk predictors: Recent research has found that counting cholesterol-carrying particles (apoB) is a more accurate predictor of heart attack risk and micronanoplastics in artery-clogging plaque than traditional cholesterol tests. Studies are measuring the complex interplay of clinical, lifestyle, and social factors like neighborhood and socioeconomic status that drive racial disparities in premature heart disease. Use of influenza vaccination improves survival and reduces readmissions in patients with advanced heart failure and virtual care and telehealth improve access to and participation in critical services like cardiac rehabilitation, especially for underserved and rural populations.
by Dr. Indrajeet Tyagi and Dr. Iranna Hirapur
A merging of revolutionary technologies and a deeper understanding of basic disease mechanisms is confident to transform the landscape of cardiovascular medicine. The latest heart disease research points toward a new era of personalized healthcare that is driven by sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI), revolutionary genetic therapies, and innovative pharmaceuticals. From refining diagnostic accuracy to tailoring treatment, these advancements are shifting the focus from a reactive, one-size-fits-all model to proactive and individualized interventions.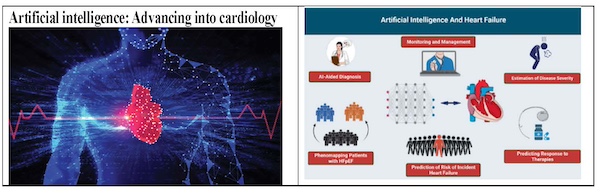
You may also access this article through our web-site http://www.lokvani.com/
